This article is based on the docker seminar on 11, November 2022 from GDSC-Yonsei. I would like to give credit to GDSC Lead for the reciprocal teaching.

Problem
A python file("hw1.py") runs well on my laptop.
But what if it does not on my friend's?
➡ ModuleNotFoundError: No Module named 'xgboost'
➡ The module isn't installed in his laptop
Plus, what if there's one who hasn't installed Python?
What if there's one with Python 2.10 ..?
It is a headache to configure your environment for different versions of software a on single machine.
Solve
"Let's make our program run in every environment!"
✅ Virtualization
Virtualization, as the name implies, is the creation of a virtual version of something, such as an OS, a server or a storage device.
It creates a simulated computing environment that is abstracted from the physical computing hardware.
Then the software simulates hardware functionality.
There are 2 types of virtualization. Let's see what are the differences.
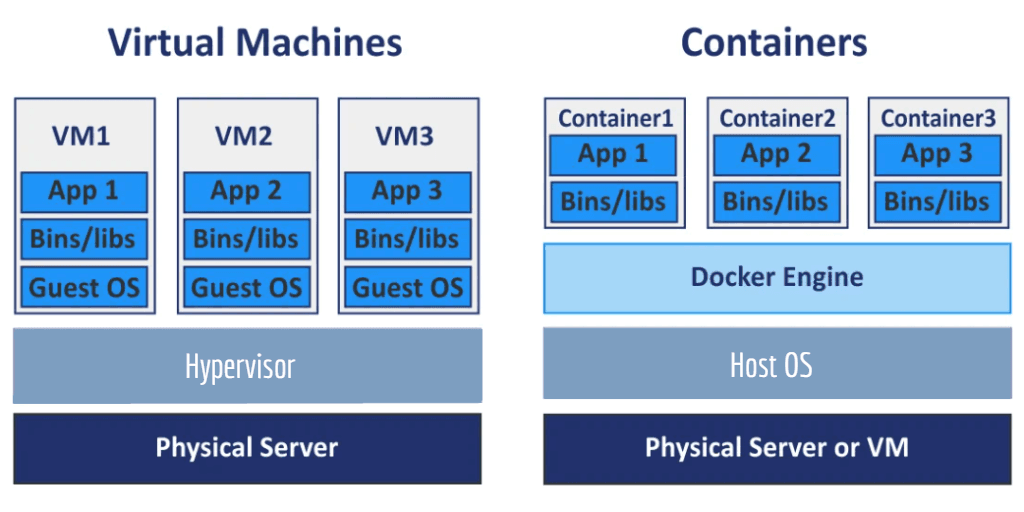
1. Virtual Machines
✌ Hardware-level virtualization
A virtual machine is a system that acts exactly like a computer.
Each virtual machine requires its own underlying operating system, and then the hardware is virtualized.
Virtual machine takes up a lot of resources because each VM runs a virtual copy of all the HW that the OS needs to run.
Hypervisor:
A layer that runs on the physical host and interacts with both the host machine and the VM.
It abstracts the host computer's resources to VM.
Thanks to the hypervisor, the hardware resources are virtualized and each VM is isolated from the other.
2. Container
✌ OS-level virtualization
Containers are a layer of abstraction above both physical machines and VMs. It sits on top of them.
While a VM abstracts a complete machine, a container only abstracts an application and its dependencies.
While a VM has its own guest OS above the host OS, which makes the VM heavy, a container shares the host OS.
✅ Docker
What is Docker?
Docker is OS-level virtualization software.
It is designed to make it easier for developers to develop, ship, and run applications by using containers.
Container
As we mentioned above, containers are isolated from one another and bundle their own software, libraries and configuration files.
They can communicate with each other through well-defined channels.
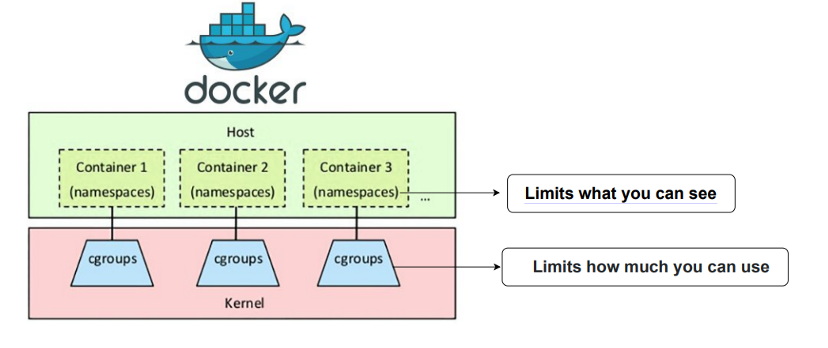
❔ Then how they are isolated?
Thanks to 2 isolation techonologies on linux kernel.
1) Namespace: a feature for partitioning kernel resources
2) Control group(cgroup): a feature for limiting and isolating resource usage(CPU, memorym, network ..) of a collection of processes.
Docker Image
Docker Image is a read-only templates containing instructions for creating a container.
Then a docker container is a running image instance. You can create many containers from same image, each with its own unique data and state.

(You can think of the left as an Image and the right as a Container! yummy Boongeobbang ;-))
(image references)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Docker_(software)
https://bikramat.medium.com/namespace-vs-cgroup-60c832c6b8c8